Evaluation of Carbon Dioxide Geological Sequestration Potential in Coal Mining Area
編號:187
稿件編號:120 訪問權限:僅限參會人
更新:2022-05-13 17:04:45
瀏覽:454次
口頭報告
報告開始:2022年05月27日 10:35 (Asia/Shanghai)
報告時間:15min
所在會議:[S10] Resource Development and Utilization of Underground Space [S10-2] Resource Development and Utilization of Underground Space-2
暫無文件
摘要
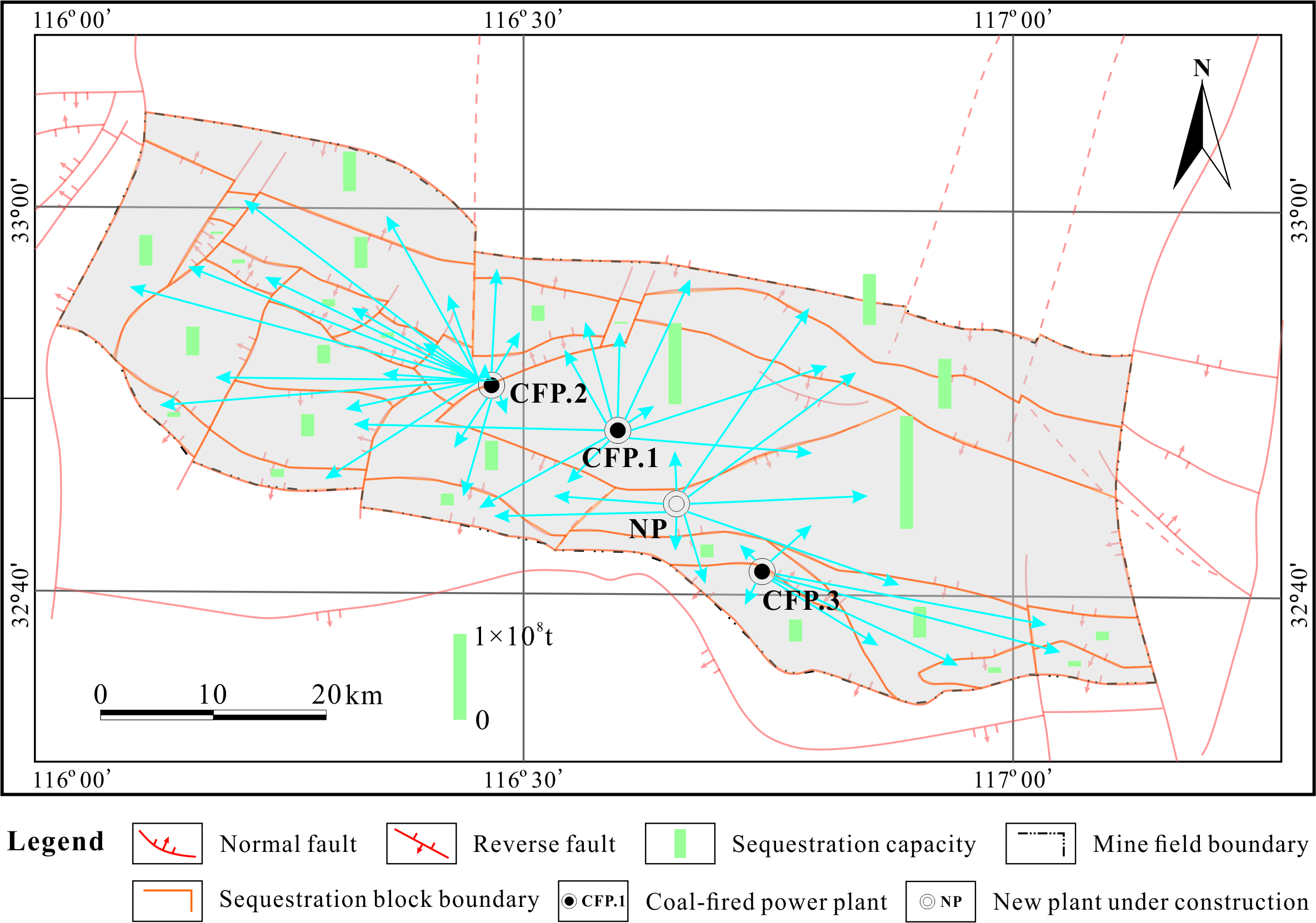
Coal bases are the concentration areas of coal exploitation and use in China in which the carbon emission sources are concentrated, and carbon emission reduction is challenging. However, the carbon emission sources and geological sequestration sinks typically correlate well with coal bases, providing favorable conditions for clustering carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS). CCUS is the only way for coal bases to achieve near-zero carbon emissions in the future. This study established the constitutive equations of CO2 sequestration capacity for unexploited deep coal seams, residual coal in producing and abandoned mines, and mined-out areas based on their CO2 sequestration form, geological background, and coal mining status. Then, the geological sequestration potential of one of the most important coal bases in east China was discussed according to the constitutive equations of CO2 sequestration capacity by considering matching relationships between sequestration sources (coal-fired power plants) and sinks. The results showed that the coal base has excellent CO2 geological sequestration potential. The total CO2 sequestration capacity in coal seams is approximately 0.85 billion tons, including 0.76 billion tons in unexploited deep coal seams, 5.17 million tons in residual coal in producing and abandoned mines, and 82.45 million tons in mined-out areas. The source–sink matching relationships of CO2 geological sequestration in the coal base provide favorable conditions for CCUS, and the average distance between the CO2 sequestration sources and target sequestration sinks is only 10 km. The unexploited deep coal seams with buried depths of 1000–1500 m are primary reservoirs for CO2 geological sequestration in the coal base. In the next 30 years, CO2-enhanced coal bed methane recovery (ECBM) in unexploited deep coal seams and CO2 sequestration in mined-out areas should become a special CCUS technology in the coal base due to their great CO2 geological sequestration potential. CO2-ECBM and CO2 sequestration in mined-out areas are also significant for other coal bases in China.
關鍵字
deep coal seam,residual coal,mined-out area,geological sequestration potential,source and sink matching,coal base
報告人
Shiqi LIU
China University of Mining and Technology1984年9月生,博士,中國礦業大學研究員、博士研究生導師,碳中和研究院副院長,江蘇省低碳技術學會碳捕集利用與封存(CCUS)專業委員會秘書長。《中國礦業大學學報》、《石油學報》、《煤炭學報》、《煤田地質與勘探》、《沉積學報》、《煤炭科學技術》青年編委會委員,《石油科學通報》執行編委。江蘇省“六大人才高峰”高層次人才、“2019年度江蘇省低碳技術學會拔尖青年科學家”。
主要從事煤系非常規天然氣勘探開發(煤層氣、煤系氣、頁巖氣勘探與開發)、碳中和地質技術(CO2地質封存與地質利用、煤層甲烷減排)等領域的科研工作。主持包括國家自然科學基金面上項目、國家自然科學基金青年基金、中國工程院院地重大咨詢研究項目課題、中國博士后基金面上資助項目、江蘇省自然科學基金面上項目在內的研究項目10余項。獲得省部級科技成果二等獎1項,行業科技獎勵2項。授權國際專利(美國、澳大利亞)8項、國家發明專利16項、軟件著作權4項。發表學術論文60余篇。
發表評論